In this C example[from refixed coder], the multiplication of two values program using call by reference will teach us how to pass parameters using a function(i.e. parameterized function). Some concepts are required that help us to solve this program more efficient way.
REQUIRE -
- basic variable declaration
- how to create a function in c
- pass address of a variable as an argument in a function
ALGORITHM:
STEP 1: START PROGRAM
STEP 2: DECLARE TWO VARIABLES (HERE WE WILL USE INTEGER)
STEP 3: TAKE TWO INPUTS FROM THE USER.
STEP 4: DECLARE FUNCTION AND PASS TWO INTEGER AS FUNCTION PARAMETERIZED WAY
STEP 5: DO MULTIPLICATION OPERATION IN FUNCTION
STEP 6: AFTER THAT, IN THE MAIN FUNCTION, PRINT RESULT
STEP 7: STOP THE PROGRAM
CODE:
#include<stdio.h>
long int mul_cal_ref(int*,int*);
//from refixed coderint main()
{
int first,second;
printf("Multiplication Of Two Values");
printf("Using Call By Reference in C\n");
printf("\n\nENTER FIRST NUMBER: ");
scanf("%d",&first);
printf("\n\nENTER SECOND NUMBER: ");
scanf("%d",&second);
//call by reference
printf("\nRESULT : %ld\n",mul_cal_ref(&first,&second));
return 1;
}
long int mul_cal_ref(int *a,int *b)
{
long int res;
res=(*a)*(*b);
return res;
}
CODE IMAGE:
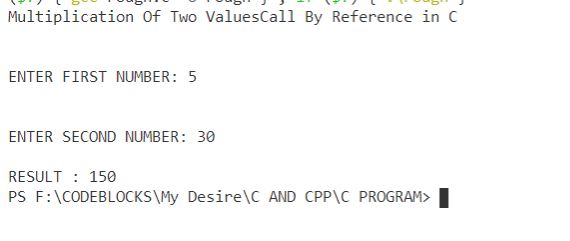
OUTPUT:
Multiplication Of Two ValuesCall By Reference in C
ENTER FIRST NUMBER: 5
ENTER SECOND NUMBER: 30
RESULT: 150
EXPLANATION:
- we have created mul_cal_ref(int*,int*) function and it's return type long int.
- using '&' before interger (such as ->mul_cal_ref(&first,&second)), we passed address of first and second variables.
- mul_cal_ref(int *a,int *b) ---'*a' and '*b' pointers take the address of first
- and second variables address.
- we have done operation in function mul_cal_ref.
- At last, we have printed the result.
Ask any queries related to programming in the comment below.




2 Comments
It is helpful to me ..tnq bro
ReplyDeleteThank you.
Delete